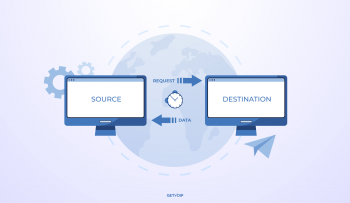
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) phones are devices that can be used to communicate through phone lines without a cord connecting the handset and base. The analog technology used in earlier cordless phone models typically resulted in sound quality that was not always very good. With digital technology, the sound is clearer, the distance between the phone and the base station can be greater, and a wider range of frequencies are available.
Originating in Europe, where DECT is the universal standard, it has since been adopted by Australia, and most countries in Asia and South America. Due to frequency discrepancies, the adoption in North America was delayed by U.S. regulations.
Connectivity for DECT must be made through a fixed network, and a gateway to connect calls to the fixed network. In most cases, the gateway connection is to the public switched telephone network or telephone jack, with connectivity over the Internet with newer technologies like VoIP [of course]. There are also other devices such as some baby monitors that utilize DECT, but in these devices there is no gateway functionality.
DECT is a key element to PBX installations in business, especially since the onset of migration from PBXs to Hybrid PBX solutions. Manufacturers such as Lantiq, Ascom Wireless Solutions, Aastra Technologies, Philips, snom and Polycom have developed IP-DECT solutions where the backhaul from the base station is VoIP (H.323 or SIP) while the handset loop is still DECT. These solutions are sometimes restricted by the cost of the base station but may be economical where the concentration of users is high.
DECT and Wi-Fi base stations are roughly equivalent in price, though DECT base station coverage is about double that of Wi-Fi – sometimes spanning over 300 feet. PBX networking vendors such as Cisco promote the adoption of handsets that use VoIP over local Wi-Fi as the replacement for DECT, but this imposes significant overhead on the design and complexity of the Wi-Fi network in order to provide roaming, coverage and reservation of bandwidth, not to mention quality of service.
DECT phones, commonly known as DECT 6.0 in the US, require a base station to both charge the handset and receive the phone’s signal. They are especially useful in homes with multiple floors or large layouts, and for offices that want several cubicles to access the same phone system.
Check out Grandstream’s recently released Cordless VoIP DECT phones and their capabilities
Additional Reading
Wireless Phone Standards: DECT vs Bluetooth
Jabra’s Mystery Gift: Our Hands-on Review of the Engage 75 Headset
The Best Conference Room Phone Systems & Hardware



![What is Omnichannel Customer Service? [Benefits & Tips] What is Omnichannel Customer Service? [Benefits & Tips]](images/omni-channel-explained-350x203.png)