When you think of the phrase “call quality,” you might assume it refers to factors like the level of customer service your agents provide, first contact resolution rates, or hold times.
However, a huge part of your VoIP phone system’s overall call quality is the quality of the audio itself.
Do your customers frequently complain of static, choppy audio, or echoing? If so, it’s likely you’re dealing with call latency, and you’ll need to take a VoIP latency test to understand just how serious the issue is.
Surprisingly, top-tier tech professionals say that eliminating excessive latency is one of the biggest three IT factors influencing overall business success, right alongside cybersecurity and bandwidth cost.
But what exactly is latency, and how will reducing it improve your business?
Even more importantly, what causes latency and how can you fix it?
Table of Contents
- What Is Latency?
- How Latency Impacts Your Business
- What Causes Latency and How Can You Fix It?
- Measure Latency with a VoIP Latency Test
- VoIP Latency and Call Quality FAQs
What Is Latency?
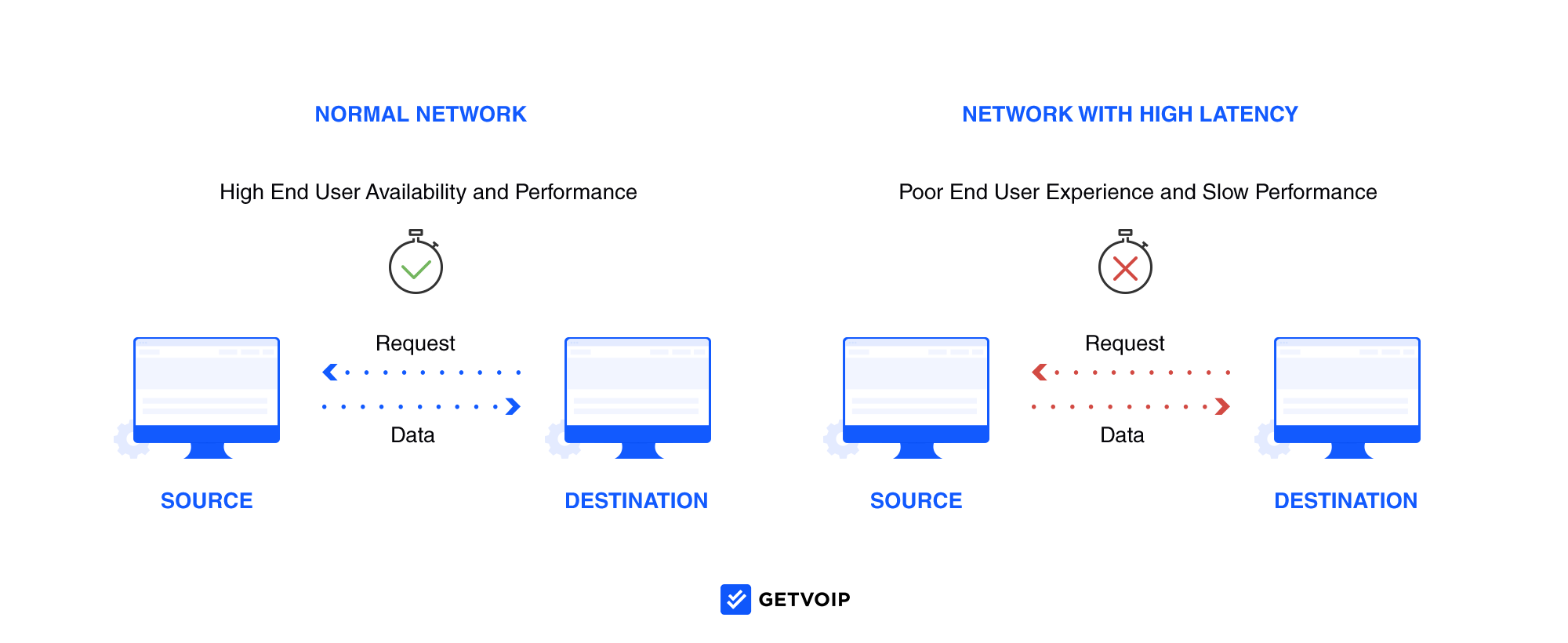
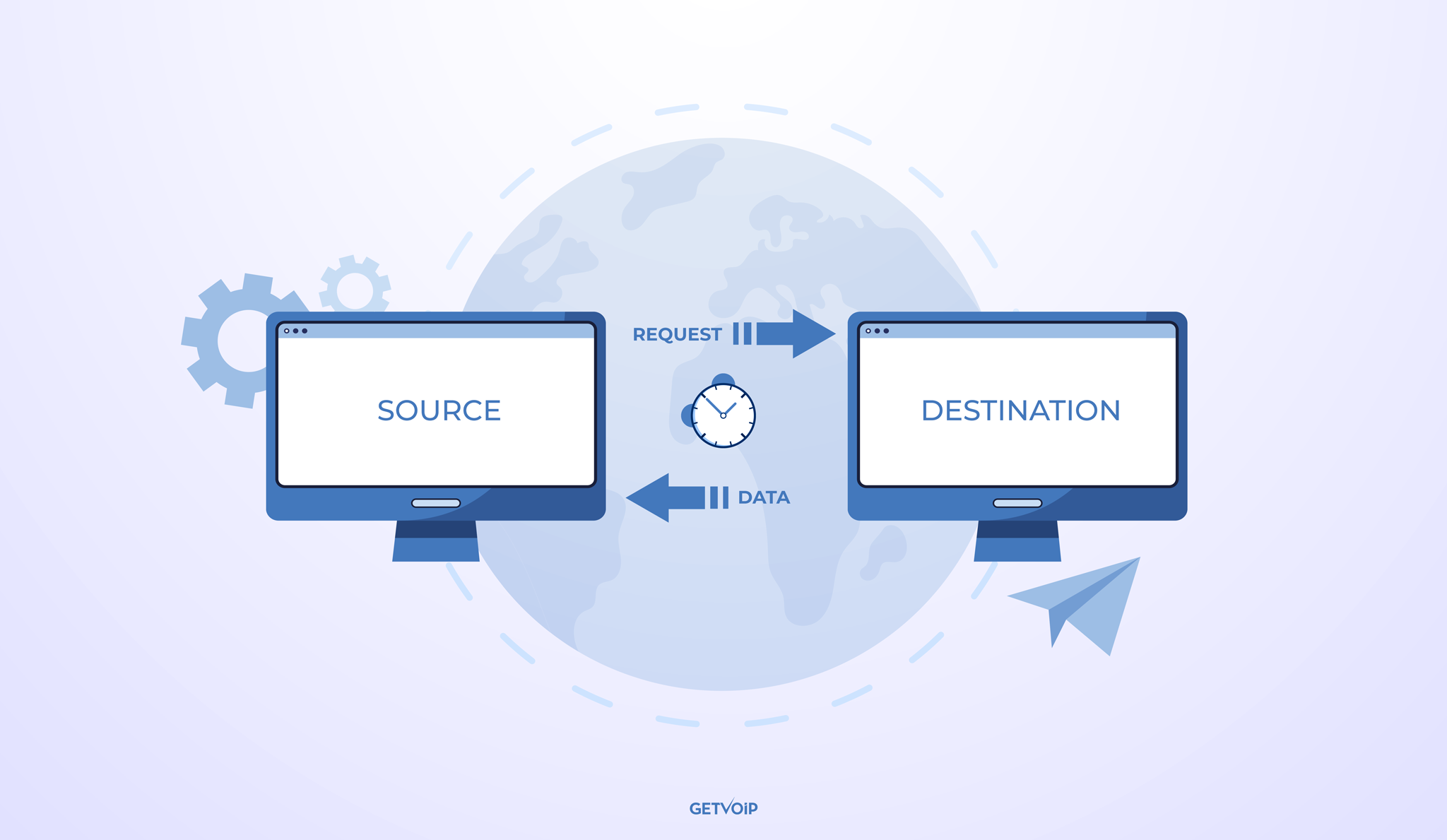
Latency is the lag in response time between when a network user initiates an action and when the corresponding action is completed.
During that delay, data is transferred from one endpoint to another – and sometimes, that data can take longer than we’d like to arrive at its destination, resulting in latency (more on specific latency causes later.)
Easily recognizable examples of latency include the rainbow-colored spinning “beachball” on a Mac laptop, the delay between when you click on a YouTube video and when it starts playing, a slow loading web page, or the time between when you power on your cellphone and when you’re actually able to use it.
In business VoIP specifically, latency is the amount of time it takes for voice data packets to travel over the Internet from the outbound caller to the inbound caller. In simpler terms, VoIP latency refers to the delay between when you speak and when the person on the other end of the line hears what you’re saying.
VoIP data is transmitted via data packets, which are compressed digital files made up of raw audio (AKA, your speaking voice.) These data packets are then sequentially sent through the source device, the router, the VoIP platform’s server, a carrier network, and finally, to the recipient’s device and back again when they respond.
Given the complexity of that journey, it’s no wonder that latency, while frustrating, is quite commonplace in VoIP and any other business phone service that relies on the Internet.
Problems start when that latency rate becomes excessive and begins to interfere with your ability to communicate via VoIP solutions.
How Is Latency Measured?
Latency is measured in milliseconds, (ms) and the ideal latency for VoIP telephony is 250ms or less.
However, a recent study shows that over 90% of executives expect a latency of 10ms or less in order for their applications to succeed, with over 75% insisting on 5ms or less.
Either way, anything above 250ms begins to noticeably impact the quality of your voice calls.
There are two ways to assess your current latency levels.
The first (and most common) way is one-way latency, which measures the amount of time it takes a data packet to travel from the source network to its destination.
Two-way latency (sometimes called round-trip time latency) measures the amount of time it takes a packet to be transmitted back and forth from the original source, to the destination, and back to the original source again.
How Latency Impacts Your Business
Increased latency can negatively impact your call quality in numerous ways, frustrating both team members and clients.
But it’s not just your customer satisfaction score that will take a hit because of high latency.
Past studies have shown that even an extra 100ms of latency can cost you roughly 1% of your sales. Especially if you work in industries that rely on lightning-fast speed for success — like trading on Wall Street — those extra 100ms could cost you even more.
Other issues commonly caused by slow data transmission include:
- Speakers unwittingly interrupting each other
- Speakers accidentally talking simultaneously, overlapping one another
- Echoing, making it difficult to differentiate between speakers
- Out-of-order conversations (hearing the ending of a sentence before the beginning, hearing only the middle part of someone’s sentence, etc.)
- Frozen video calls
- Audio on a video call is out of sync with the video stream
- Completely derailed conference calls with 3 or more participants
- Delayed or dropped calls
- Slow download speeds and upload speeds
- Internet connectivity issues
- Loss of real-time communication
- Static audio
- Choppy, garbled, and incomprehensible audio
What Causes Latency and How Can You Fix It?
There are several possible causes for latency in your virtual phone system, and many of them are things you’d never suspect could have such an impact.
Below, we’ll explore some of the most common reasons for the lag and provide actionable solutions for how to troubleshoot it.
Too Much Distance Between Servers
Sometimes, latency happens because there’s an excessive distance between the server/system making the request and the one that responds to it.
If you haven’t yet chosen a VoIP provider (or if you’re thinking of making a switch) ensure that they offer numerous national and international server locations and IP addresses. The more data centers they have, the more likely it is that you’ll be able to achieve low latency levels.
Not Enough Bandwidth
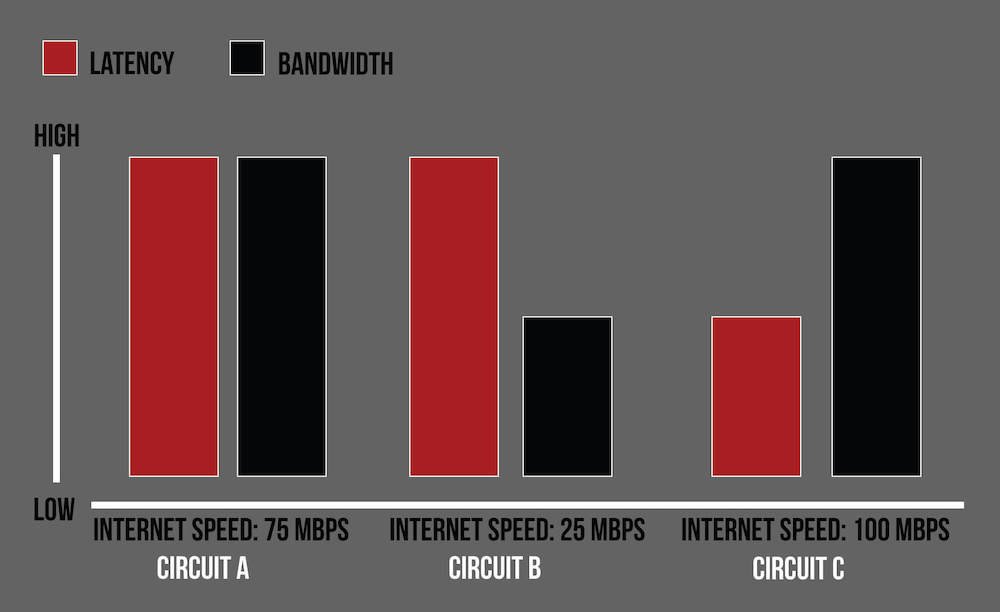
Along with server location issues, a lack of sufficient bandwidth is one of the leading causes of latency issues.
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that your Internet connection can transmit over a set period of time (note that it doesn’t refer to your Internet speed, just the amount of data it can get from one place to another within a certain timeframe.)
If you have a VoIP phone system, you’ll likely need to upgrade your bandwidth to prevent increased latency and other issues. The amount of bandwidth you’ll need depends on the number of concurrent calls your business makes.
Bandwidth is measured in megabits per second (MBPS). The average bandwidth is 12-25mpbs.
Upgrade your bandwidth, and also consider using a VLAN to segment your network.
Outdated Hardware
If a lack of bandwidth isn’t the issue, it’s time to take a look at your hardware.
Can’t remember the last time you upgraded your router? Have you been forced to rely on wireless connections to make calls because of faulty equipment?
If so, then it’s definitely time for an upgrade – consider VoIP routers specifically designed for virtual phone systems.
Also, be sure you also check to make sure that wires, cables, modems, and ports haven’t been bent or damaged in any way. What about headsets or microphones?
If they have been, they’ll need to be replaced as well.
Issues With Internet Connection, ISP Quality, or VoIP Provider
Sometimes, the simplest solution really is the best one: ensure that your network connection is configured correctly, that all Ethernet cords are completely plugged in,
Of course, most of the time, the problem is a little more complicated — and is often an issue with your Internet Service Provider.
Sometimes, your ISP uses a codec (which is what turns voice signals into digital packets) that isn’t compatible with your VoIP system. Depending on your provider, you may be able to switch to a compatible codec, but if that’s not possible, you’ll need to switch Internet providers.
You should also contact your VoIP provider to see if they have any troubleshooting tips, as chances are, they deal with this sort of issue often.
Quality of Service Settings
Quality of Service (QoS) settings actually allow you to prioritize bandwidth for certain devices or data — which you should use to ensure that your VoIP system is first in line for your bandwidth usage.
Bandwidth reservation, Multi-Protocol Label Switching, (MPLS) and other techniques make prioritizing bandwidth easy.
Additional Tips to Prevent Excessive Latency
If none of the above solutions worked, you could try to:
- Reconfigure your Firewall or other antivirus software settings to open ports and allow VoIP software clearance
- Turn off any unused applications and disconnected other devices when not in use
- Avoid using Wi-Fi or mobile devices to make VoIP calls whenever possible, rely on an Ethernet line instead
Measure Latency with a VoIP Latency Test
Armed with a better understanding of what VoIP latency is and why it matters, there’s one final step you need to take to see what steps you need to take to fix the issue.
Using network latency testing, sometimes called a ping test, will help you to understand how much of a lag you’re dealing with in your phone system, and can even assist you in identifying other issues affecting your call quality.
The good news?
You can use our free VoIP and Internet Speed Test Tool to get started.
Whether you end up switching Internet Service Providers, going with a better VoIP solution, or even if you find your VoIP call speed is up to snuff, our network performance monitor tool will give you the test results you need to move forward.
VoIP Latency and Call Quality FAQs
Still have a few questions? The below FAQ section on VoIP latency and call quality can help.
Many people confuse bandwidth and latency, as both can seriously impact call quality if not optimized.
Latency refers to the amount of time, in milliseconds, it takes for data to get from one place to another.
Bandwidth, on the other hand, refers to the amount of data that your Internet Service Provider is capable of transferring from Point A to Point B over a set amount of time.
Unfortunately, latency isn’t the only issue that can wreak havoc on your overall call quality.
Consider other potential issues like:
- Jitter
- Echoing
- Frequent dropped calls
- Inability to make or receive calls (loss of service)
- Feedback
In addition to taking a latency test, you can measure your current audio and overall call quality by examining your contact center’s Mean Opinion Score (MOS for short.)
Your MOS score is made up of several call quality metrics in addition to latency, such as compression, codecs, bandwidth, packet loss, and jitter. MOS scores of 4.3 and above are considered excellent.
Above all, remember that when evaluating call quality, you should consider three main factors: the listening quality, conversational quality, and transmission quality of every score.
For even more ideas, check out our article on the most important call tracking metrics to consider.
There are a variety of steps to take to improve call quality, including:
- Getting a separate router for your VoIP system to prioritize VoIP traffic
- Ensure you’re using CAT 5 or above cabling
- Purchase a high-quality headset or microphone for your agents
- Avoid making calls over Wi-Fi when possible
- Switch to a better Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- De-jitter your system with an Edge device or RTP steam
- Turn off Bluetooth when connected devices are not in use