Making the switch to VoIP phone systems from POTS saves businesses anywhere from 50%-75% on communication costs in addition to offering teams more mobility.
Especially given the rise in remote work and the expansion of business communication channels, it’s no wonder that VoIP platforms are more popular than ever.
Though Voice over IP software providers now offer advanced calling features, bundled services, and excellent voice quality, that doesn’t mean you won’t encounter problems from time to time.
This breakdown of common VoIP problems and solutions will help you to restore phone service — and sanity — as quickly as possible.
Common VoIP Problems:
- Problem: Jitter
- Problem: Echo
- Problem: Your VoIP Device Won’t Make Calls
- Problem: Choppy/Broken Audio
- Problem: No Sound Once Call Connects
- Problem: Dropped Calls
- Problem: Your Phone Doesn’t Ring
Top VoIP Problems and How to Solve Them
The specific issues you may run into with VoIP depend on your current location, now many people are connected to your network, your business’s daily call volume, and even your hardware.
However, there are a few consistent issues that both enterprise-level and small businesses face when it comes to virtual telephony and low-quality calls.
Below, we’ll outline the most common problems with business phone services like:
- Jitter
- Echo
- Devices that won’t make calls
- Choppy audio
- No sound once a call connects
- Dropped calls
- Missing phone calls because devices don’t ring
Then, we’ll provide several possible solutions and troubleshooting tips for each problem — many of which won’t even require you to reach out to IT support or your provider.
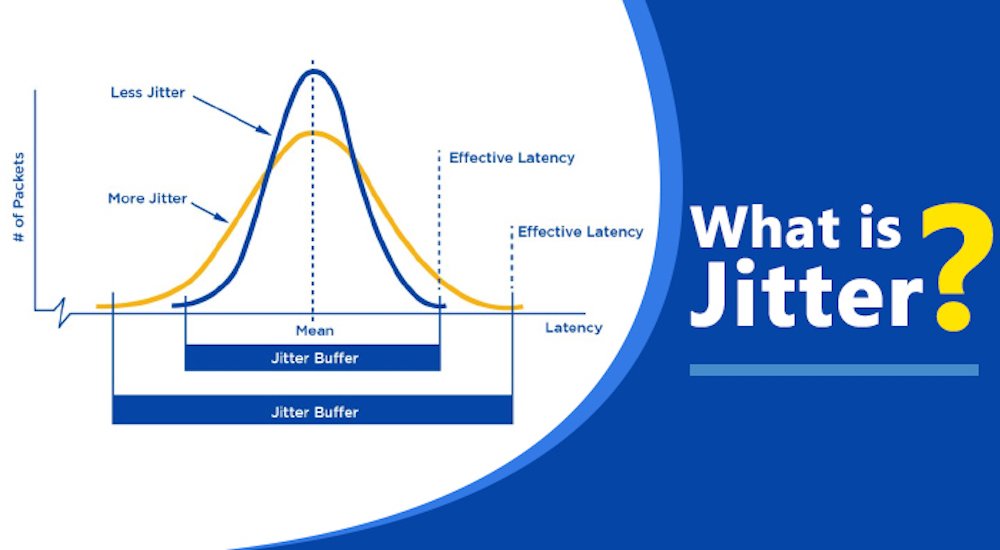
Problem: Jitter
Jitter causes pieces of your VoIP phone conversation to become jumbled, out of order, or outright missing, causing essential parts of a call to disappear or become impossible to understand.
It happens because of the millions of data packets that simultaneously travel over the same IP network. Latency — the amount of time it takes for one data packet to travel to its destination — means that some data packets may arrive earlier than others. Therefore, callers will receive parts of the conversation out of order.
Jumbled calls that last more than 30 milliseconds will impact the overall call quality, leading to drop-outs and distortion. When evaluating providers, look for those that attempt to keep the delay under 20 milliseconds.
Solutions to Jitter
The most obvious solution is to consider upgrading your Internet connectivity through your Internet Service Provider (ISP.) Your Internet may not currently have enough bandwidth to power all of your connected devices.
If you’ve eliminated network congestion and the problem persists, consider the type of Internet connection you’re using. Wireless networks are convenient and are generally strong enough to power basic Internet access, but Wi-Fi isn’t ideal for VoIP phones. Consider making the switch to an Ethernet internet connection.
Outdated modems and faulty Ethernet cords can also contribute to jitter. The same goes for your phone’s frequency. Aim for a frequency that is no higher than 2.4GHz.
Installing a jitter buffering is an additional solution, and may be able to help you avoid completely upgrading your Internet connection or hardware. Once installed on virtual phones, these jitter buffers cause delays incoming packets to prevent distortion, regrouping packets through processors that convert them to audio.
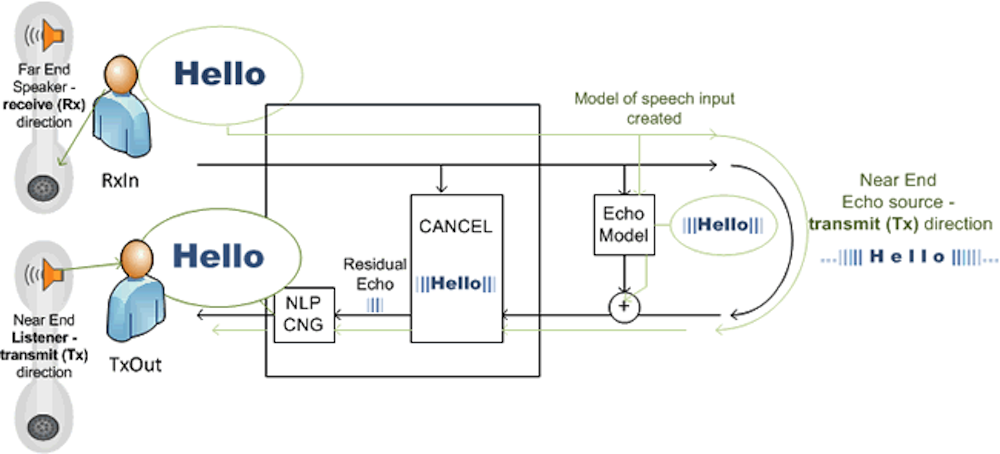
Problem: Echo
Phone echoing causes voices to repeat at varying intervals and volume levels while on a call, making it difficult to follow the conversation.
Often, the call recipient is the one who experiences most of the echo, meaning that often, the caller isn’t fully aware of the issue. In general, echos will become audible after roughly 25 milliseconds of delay.
While sometimes, echo is caused by feedback from the person you’re speaking to, most of the time, it’s due to an issue with your own VoIP phone system. Even if one person is experiencing phone echo on a conference call, it can completely derail the experience for all participants.
Solutions to Phone Echoing
The easiest way to both prevent and fix echoing is to take your phone off the speakerphone.
Though convenient, a speakerphone means that your voice is transmitted through multiple microphones and speakers over the course of the conversation. This is an especially common issue with smartphones. Instruct anyone not hearing the echo to turn down their phone’s speaker or microphone.
There may also be an issue with your current phone headset. To test this, make a call with your handset and your headset, and see if the echo occurs exclusively when using the headset. If so, it’s time for a replacement.
As with jitter, echoing can also be caused by a faulty internet connection. We recommend running an Internet speed test to evaluate whether or not your current level of bandwidth is sufficient.
Electromagnetic interference can also lead to a phone echo.
This happens when you place your devices too close to many other electronic devices. For example, if you set your smartphone on top of your laptop when making calls, you’ll likely experience poor-quality calls, as both devices have large electric fields.
Finally, in addition to checking your headset, ensure that your wall jacks, Ethernet cords, and cables are not damaged, twisted, or wet.
Problem: Your VoIP Device Won’t Make Calls
Sometimes, your VoIP platform may not allow you to make outbound calls, either by failing to connect or by displaying an “X” on the screen/interface.
Especially if you’re operating a call center, this essentially shuts down your business until the issue is resolved.
Solutions to the Inability to Make Calls
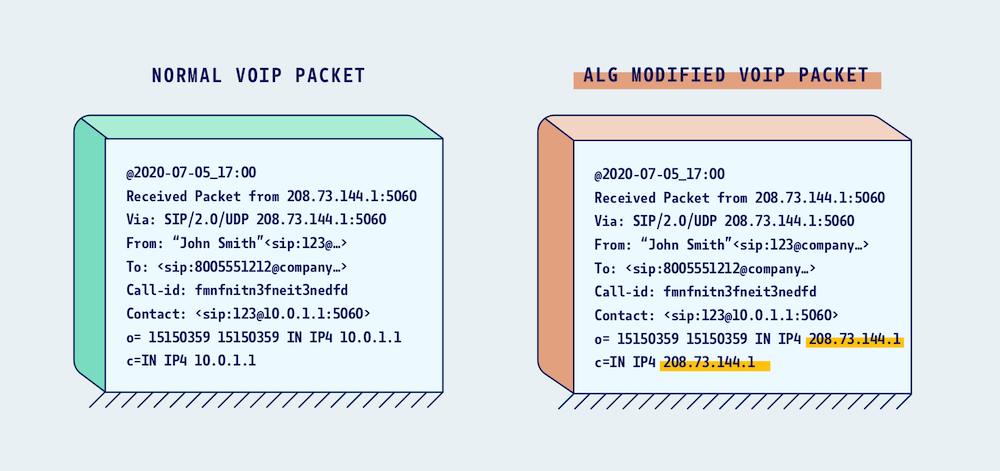
SIP ALG — Session Initiation Protocol Application Layer Gateway — is the likely culprit here.
Though present in most routers, it can cause major issues for VoIP users. When this happens, two routers aren’t able to process and transmit packets due to firewalls that disrupt internal network and VoIP traffic.
To fix this, you’ll need to turn off SIP ALG.
If that doesn’t work, then try repositioning your VoIP telephones on a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN.)
Problem: Choppy/Broken Audio
Choppy voice and audio mean that, although the call isn’t completely disconnected, certain words are dropped and voices keep cutting in and out.
It can sound like you’re driving through a tunnel, and only hearing every third word the other person is saying. It’s also one of the most common VoIP issues on this list.
Solutions to Choppy/Broken Audio
Your response to choppy audio depends on whether you’re the one cutting in and out, or if the other person is.
If you can hear the other person cutting in and out, then your download bandwidth is insufficient, and vice versa.
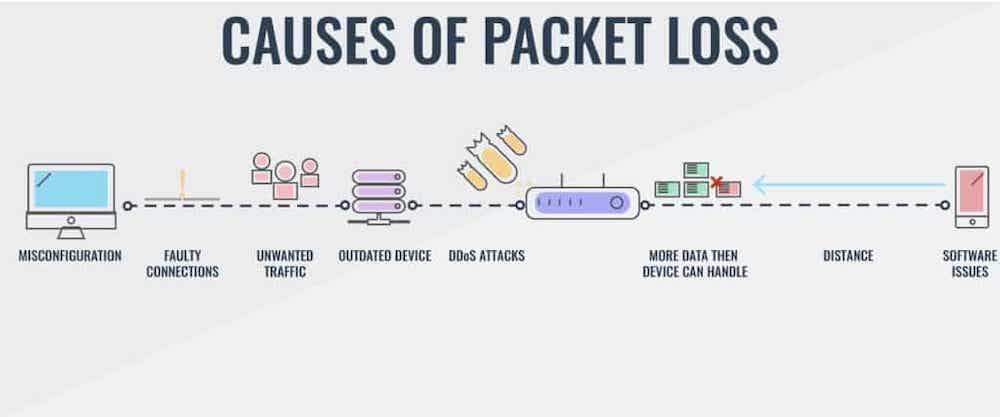
Either way, packet loss is the main culprit here. Packet loss happens when the smaller pieces of data being transmitted don’t successfully transfer. This can be caused by network latency and instability, a lack of bandwidth, or high network congestion.
Consider turning off applications with streaming capabilities, like YouTube or Netflix, that take up lots of network space. You should also ensure you’ve prioritized VoIP service on your router’s Quality of Service (QOS) settings.
Problem: No Sound Once Call Connects
In some cases, you may have no issue with connecting calls, but may not be able to hear anything once the calls have been successfully connected.
In some cases, the party you’re speaking with may not be able to hear you, even though you can hear them perfectly. These audio issues can be one-way, or neither side may be able to hear the other.
This leads to a frustrating and endless back-and-forth of “Can you hear me now?” that can throw a serious wrench in communication.
Solutions to a Lack of Sound
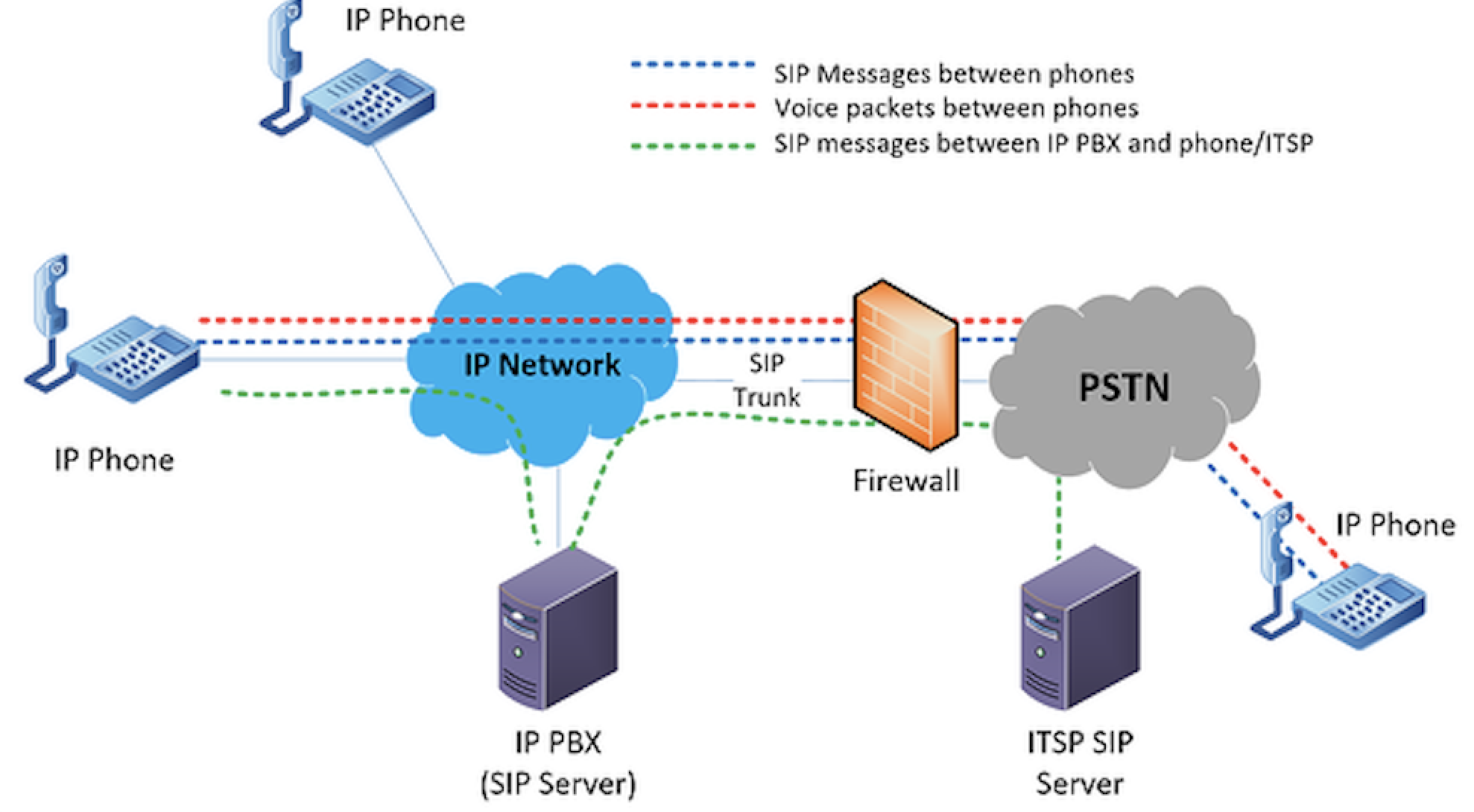
In lots of cases, a lack of sound on connected calls is due to issues with firewalls blocking RTP packets.
This causes voice packets to travel in only one direction or prevents both sides from receiving these data packets. One solution is to examine the SIP ALG (Application Layer Gateway.) In most cases, disabling it will solve the issue, as it opens ports that let traffic flow through.
You may also be experiencing incompatible codecs between two phones. If this happens, calls will be able to be completed, but no packets can be exchanged — meaning a complete lack of audio.
Ensure that both endpoints share a common codec.
Problem: Dropped Calls
Dropped calls — calls that suddenly end in the middle of a conversation without warning — are an enormous source of frustration for both employees and clients.
In addition to dropped calls in the middle of a conversation, you may also notice that VoIP calls suddenly drop after a certain amount of time.
This is especially common in call centers with a consistently high outbound call volume.
Solutions to Dropped Calls
As cliche as it sounds, the first thing to do with consistently dropped calls is to ensure that your software and any compatible VoIP hardware and equipment has been updated.
To make this process easier, we highly suggest turning on auto-updates whenever possible. Contact your provider to be certain you’re running the most current version of your platform.
Next, disconnect all the devices currently connected to your VoIP network, then reconnect them one by one to determine which one is causing the problem. If you’re using a separate caller ID tool, a dial-up modem, or an alarm system on your network, these devices may be what’s causing the issue.
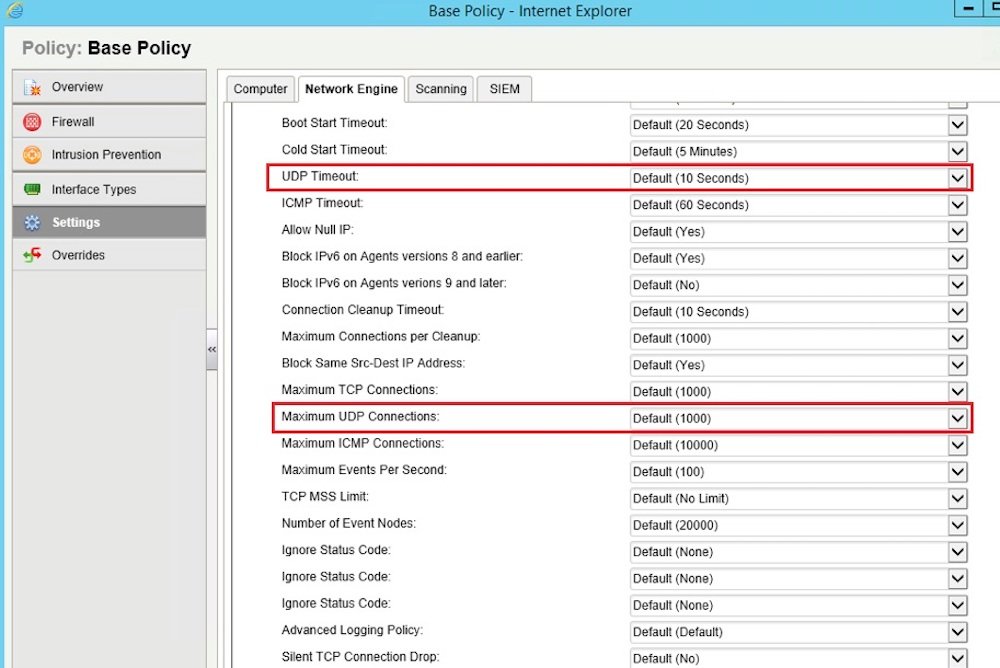
If calls seem to drop after a specific amount of time, then the problem may be that your provider has set up automatic disconnects after a set number of minutes to ensure that the calls are not invalid open calls. This process is known as a UDP Timeout — the end of the length of time that the UPD is connected to a router or firewall.
If your calls often last longer than this amount of time, contact your provider and ask them to remove the safety disconnect. In the meantime, let clients know that you’ll need to hang up and call them back if the phone call lasts for longer than the specified time period.
You should also change your router settings to increase the timeout to at least 60 seconds. You can also change devices to Transmission Control Protocol, (TCP) from UPD, as this allows for the retransmission of lost voice packets.
Problem: Your Phone Doesn’t Ring
Whether you’re waiting on a call back from a coworker or a client, if your phone sends your calls straight to voicemail instead of ringing, these missed calls can cause serious delays in productivity — not to mention potential lost revenue.
In some cases, you may find that your VoIP system skips your office phone altogether and sends calls directly to another device.
Solutions to Missed Calls
Luckily, one of the biggest problems also has one of the easiest solutions.
First, check to ensure that your phone is still registered with your current VoIP provider. If not, contact the company and learn how to re-register your devices.
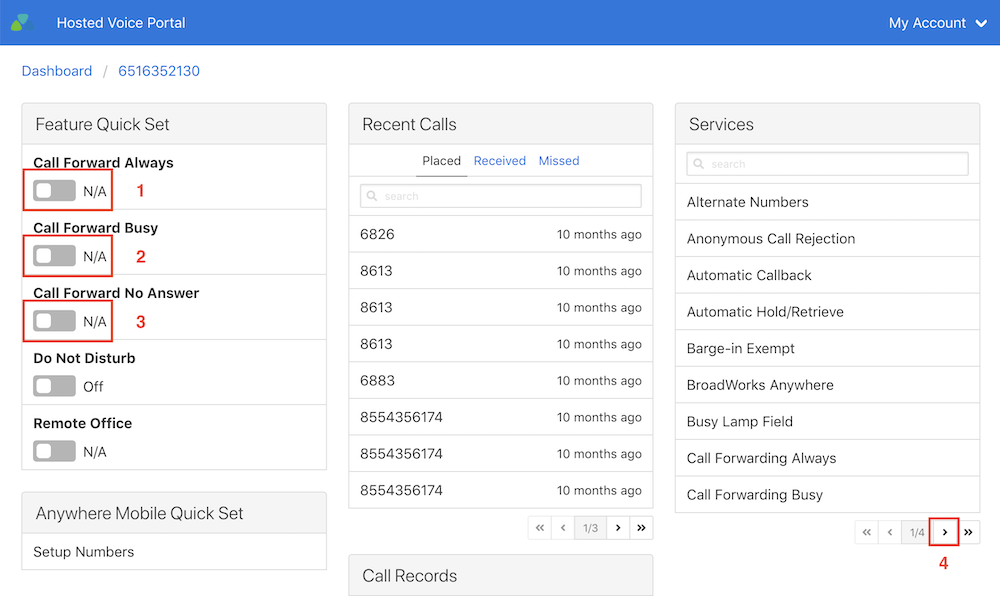
You may have also accidentally left your phone on its Do Not Disturb setting.
Finally, take a second look at your current call forwarding settings. You may have accidentally adjusted the configuration or forgotten to reset back to your standard settings.
What To Look for In A Business VoIP Provider
Though this list may be able to help you solve some of the most common VoIP problems, in order to have the highest VoIP call quality experience, the most important step is to choose the best possible software.
When evaluating providers, consider their guaranteed uptime, customer support options and availability, and whether or not they provide training for their systems.
Looking for more advice about the features, integrations, pricing, and hardware to consider when making the switch to VoIP?
Our table of the top business VoIP service providers breaks down some of the most popular software on the market today, giving you the foundational knowledge you need to compare plans and make an informed decision about your business communication system.