Business VoIP is the new normal in both remote work and in-office communication.
Roughly 46 million VoIP phone lines exist today, and that number is only growing thanks to the higher call quality and advanced features that Voice over Internet Protocol provides.
VoIP solutions offer numerous advantages over traditional phone lines, especially when it comes to overall pricing and cost savings.
Whether you’re ready to switch to virtual telephony for the first time, or if you’re upgrading to SIP trunking from Hosted PBX, you’ll need to consider the cost benefits, the level of IT support required, scalability of services, and more.
Learn about the main differences between Hosted PBX vs SIP trunking, the pros and cons of each option, and which one is the best fit for your business.
Table of Contents:
- What is Hosted PBX?
- What is SIP Trunking?
- SIP Trunking vs Hosted PBX
- Other Business Communication Tools
- FAQs
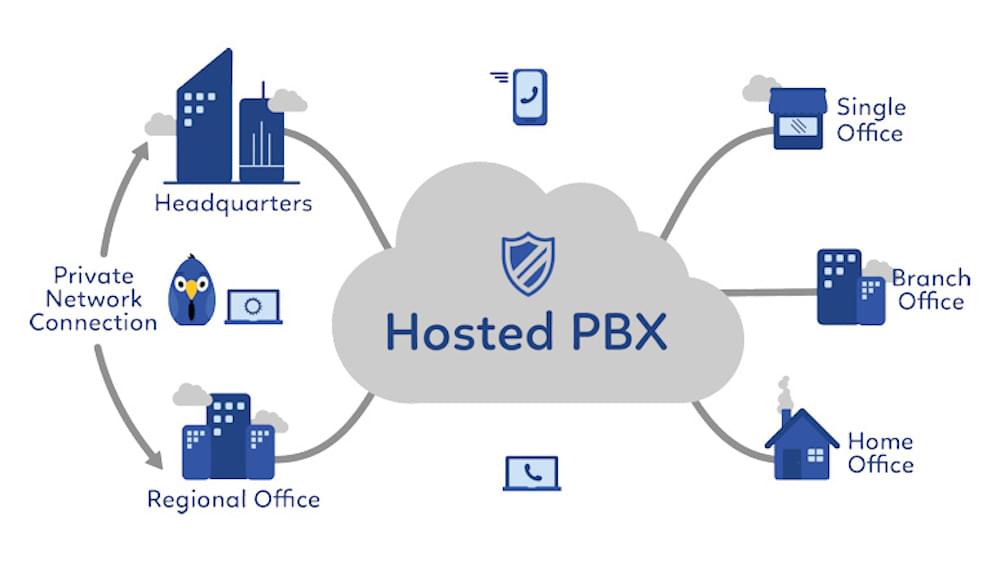
What is Hosted PBX?
Hosted PBX (Private Branch Exchange,) is an offsite business VoIP phone system. It does not require any on-premise equipment or in-house IT staff to operate or maintain, as it is entirely managed by the third-party Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP.)
Think of hosted cloud PBX systems as similar to website hosting.
While you can build out your website, update it, and use all of its features and functionalities at any time, you don’t have to worry about having an on-premise server. The same thing goes for your virtual IP PBX solutions.
In a sense, you’re “outsourcing” the technical side of your business phone to the third-party provider of your IP phones. Internal changes, like adding new features or an additional number of users through the admin portal, are the only things you need to handle.
A Hosted PBX system connects your business phone directly to the Public Switched Telephone Network, (PSTN) and one network will provide users with several telephone lines. To get started with Hosted PBX, you’ll only need your desired business telephones, a broadband Internet connection, and wireless routers.
Users can access their business phones from any device in any location with an Internet connection.
Recent studies show the Hosted PBX market will be worth roughly $9.5 billion by 2023 — nearly a 15% growth from 2018.
The technology is especially popular in the healthcare sector since PBX offers high-quality, real-time communication with patients.
It’s also popular among e-commerce shops that don’t want to keep customers on hold for too long, and that use autoresponders and self-service IVR to let customers get the information they need quickly.
Advantages of Hosted PBX for Business Owners
The biggest advantage of going with a hosted PBX solution is having someone else provide the phone system’s server and manage things like updates, maintenance, or downtime.
Because there is no need for excessive hardware or a lengthy installation, these phone systems can often be set up within a single business day. Plus, not having to purchase expensive equipment keeps setup costs low, often in the range of a few hundred dollars.
Additionally, you won’t have to pay to hire a technician to fix a problem if you experience a loss of telephone service — the provider will take care of that for you.
Common PBX capabilities include features like call forwarding, call routing, call transfers, automated attendants, and voicemail.
Your monthly cost is determined by the number of telephone lines/users and features you’ll need, though some providers charge by the minute. In general, your cost will range from $15-$50/telephone line per month — a much higher level of cost-efficiency than traditional phone systems.
This makes a virtual PBX phone ideal for small businesses and startups that operate out of a single location.
Most businesses with 25 employees and under, as well as those who don’t usually make a high number of concurrent daily phone calls, opt for a PBX service. Note that, if you plan on exponentially increasing your number of employees, you may need to make the switch to a SIP trunking service.
Disadvantages of Hosted PBX
The main downside of hosted PBX phone service is the fact that call quality is entirely impacted by your Internet connection.
Without a stable Internet connection and an accurate estimate of your company’s highest potential call volume, audio quality can decrease while dropped calls increase. Consider your daily number of concurrent calls, and speak to your provider about the required kilobits per second speed. Normally, the minimum is 90 kilobits per second.
Additionally, some companies don’t like the fact that with hosted PBX, the security of their business phone is left up to the provider. For companies that work within industries that carry a high level of compliance regulations, such as healthcare and finance, this isn’t ideal.
Make sure to ask detailed questions about a potential provider’s security standards.
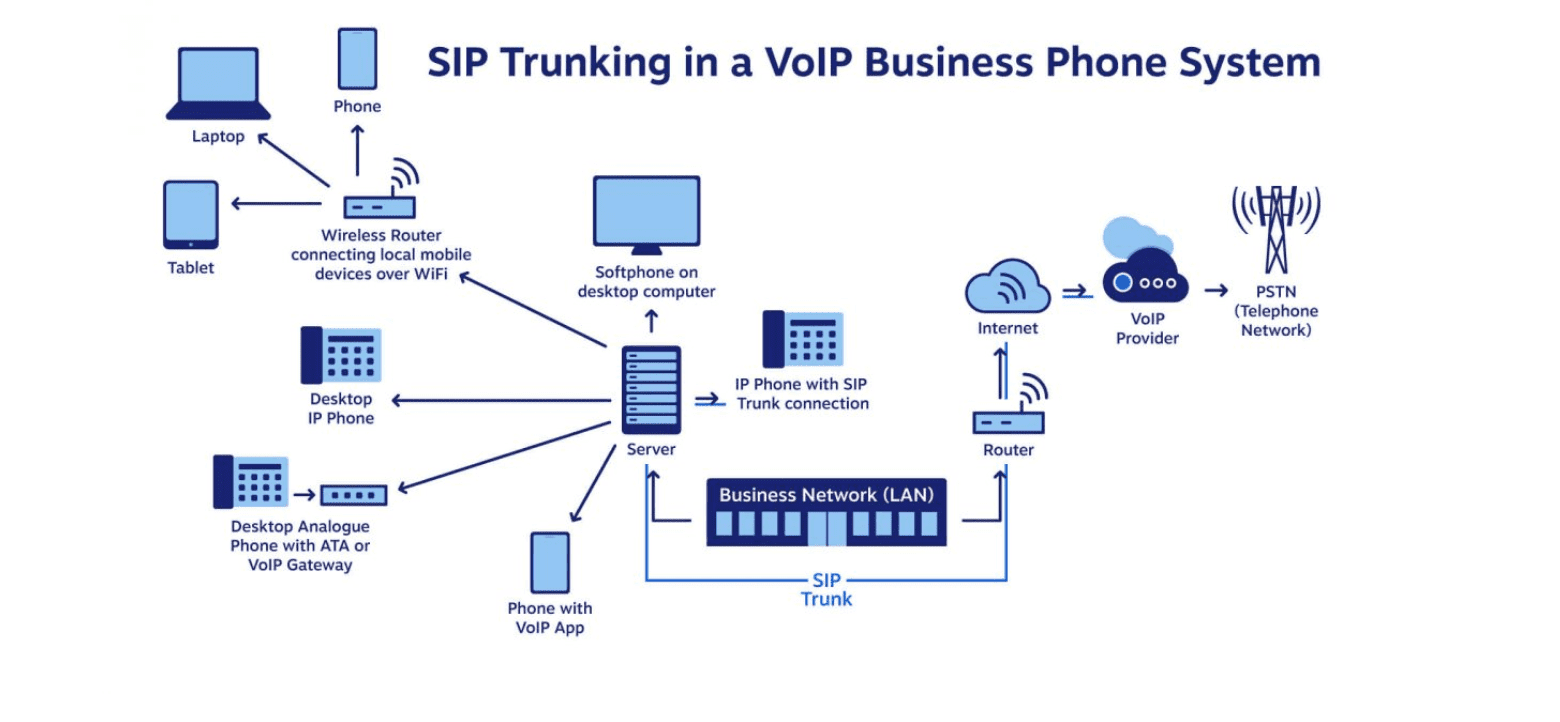
What is SIP Trunking?
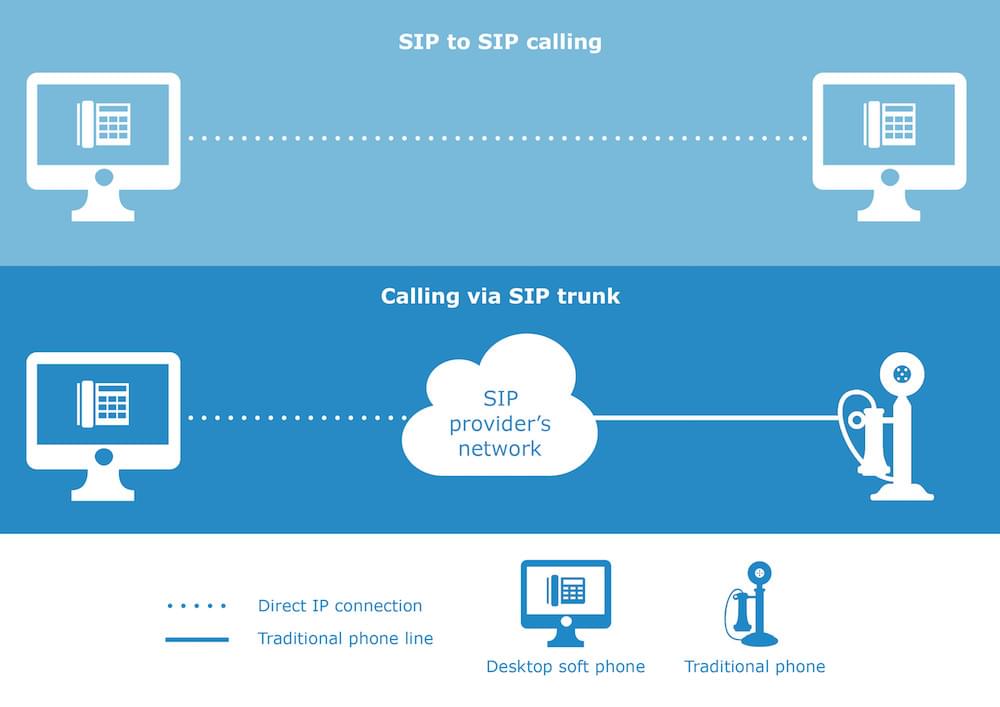
SIP trunking, or Session Initiation Protocol, is a VoIP business phone system that uses your on-premise PBX to connect to the Internet, allowing your team members to make and receive calls without excessive on-premises equipment.
With SIP trunking, your business will be responsible for obtaining and maintaining its own on-site PBX, meaning you’ll need an in-house IT staff in addition to required hardware.
SIP trunking is a gateway that directly connects your existing hosted PBX service with an ISTP. It allows employees to make and receive a high volume of simultaneous audio and video calls.
You can add numerous telephone lines and take advantage of different communication channels simultaneously, as opposed to relying on separate structures for different types of communication.
Usually, the cost is determined by the company’s number of trunks or virtual connections. In general, you can expect to pay anywhere from $20-$50/month per channel/user, depending on the number of trunks and features you choose.
A SIP trunking telephone system is best for large companies with well over 20 employees, remote teams, or companies with multiple locations. It’s also ideal for businesses with a high daily call volume, or companies that plan to exponentially increase their current number of employees. The majority of companies that have on-premise PBX equipment make the switch to SIP trunking.
Note that a PRI (Primary Rate Interface) phone system creates a physical connection between the PSTN, allowing multiple phone lines to connect to up to 23 voice channels per trunk. In contrast, SIP trunking offers a virtual connection.
SIP Trunking Advantages
The biggest advantage the SIP trunking offers is a higher level of security.
Because the server is onsite and managed by your IT staff, you’ll have total control over security protocol. Better security is also possible because SIP trunks don’t connect via the public Internet. You’ll even enjoy the added benefit of less bandwidth use.
This is especially ideal for businesses that have rigorous compliance regulations to follow.
Trunking also offers a higher overall level of call quality than Hosted PBX, because you have a dedicated telephone line. Plus, even if that dedicated telephone line fails, you’ll have a backup connection to rely on. To ensure the highest possible level of call quality, look for SIP trunking providers that operate over Tier-one carriers.
SIP trunks even let you choose the specific number of channels you need, as opposed to forcing you to buy lines in increments of 10-15.
Finally, customers will appreciate the fact that, with SIP trunks, they can use just one phone number to reach anyone in your company.
Studies show that by the year 2030, the SIP trunking industry will be worth roughly $35.5 billion.
SIP Trunking Disadvantages
Depending on whether or not your business has PBX equipment on-site already, your initial startup costs may be a bit higher than they would with a hosted PBX provider.
You may need to purchase a business Voice over IP gateway in addition to the equipment. This could run you up to $2,000 depending on your specific needs. Additionally, you’ll need to pay an on-site IT staff to maintain and update your servers.
The good news is that SIP monthly bills are often much more affordable than traditional business phones.
This is especially ideal for businesses that have rigorous compliance regulations to follow.
SIP Trunking vs Hosted PBX
The comparison table below outlines the main differences between SIP trunking and Hosted PBX.
| Features | Hosted PBX | SIP Trunking |
| Lower Monthly Cost | ✓ | X |
| Better Overall Value | X | ✓ |
| Lower Installation Fees | ✓ | X |
| Requires On-Site IT Staff | X | ✓ |
| Requires Existing PBX Equipment | X | ✓ |
| Provider Manages Updates/Troubleshooting | ✓ | X |
| Higher Call Quality | X | ✓ |
| Right for Small Businesses | ✓ | X |
| Right for Enterprise-Level Companies | X | ✓ |
| More Control Over Security Protocols | X | ✓ |
Other Business Communication Tools
Though virtual telephony is certainly an essential business communication channel, it’s far from your only option.
For example, recent video conferencing statistics show that 45% of team members use video calling platforms daily or weekly. In addition to web conferencing solutions, consider live chat software and contact center tools that allow for omnichannel unified communications across phone systems, website chat, and social media.
Larger companies fielding an especially high number of calls may want to consider call center software, which offers additional VoIP services and features.
To learn more about the top business communications systems, as well as which tools best suit the size of your business, rely on our interactive comparison tables and learn more about the best VoIP providers.
Given that VoIP calling now saves companies roughly 75% on their calling costs, now is the perfect time to rethink your current office communication.
FAQs
Below, we’ve answered some of the most common FAQs about SIP trunking and hosted PBX.