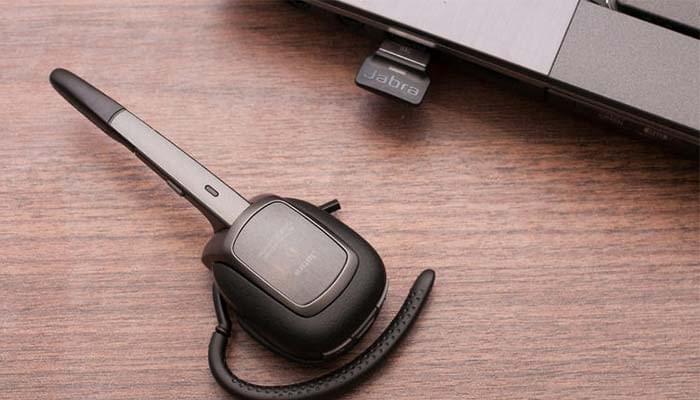
If you’ve been searching around for wireless office call centerheadsets or even cordless office phones, chances are you have stumbled across either DECT or Bluetooth options. Many of us are already familiar with Bluetooth, the standard for mobile phone connections to cars, headphones and even mice and keyboards to our computers – but what about DECT? We decided to open up the DECT vs. Bluetooth debate to see who, if at all, is the clear winner.
If you’re familiar with VoIP, you may be familiar with DECT, but the differences between the two are not so clear. When purchasing new technology for the office, there is not so much a gold standard of DECT or Bluetooth over the other. It will really come down to how your workers will utilize the technology. Both Bluetooth and DECT have their own benefits and advantages, but which you adopt will depend on how your office functions.
What is DECT?
DECT, or Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (or Digital European Cordless Telecommunications), is a wireless standard mainly used for cordless telephone systems and accessories. DECT originated in Europe, which explains the European part of the name, and is actually the universal standard in almost every market except North America.
As the major standard for most of the world’s markets, DECT is utilized for both consumer and business VoIP phones, and can be used with either a PBX or wireless LAN. Even baby monitors can take advantage of DECT.
To put it simply, the main reason DECT is not the standard in North America is due to U.S. radio frequency regulations. In order to avoid interference, DECT 6.0 was developed for the NA market simply to utilize a slightly difference frequency. Because of this, DECT headsets and phones in North America will not be compatible with other markets, but are otherwise exactly the same.
Connection of DECT devices is done through a “base station” – phones and headsets will be connected and linked to a base station, as opposed to directly to the computer (or phone for headsets) themselves. While this adds an extra layer of hardware, one base station can power multiple devices – and can be stringed together through an office to create a usable range far superior to anything Bluetooth could manage.
What is Bluetooth?
While most of us will be familiar with Bluetooth, it still serves to offer a quick introduction and recap of the technology to offer a proper comparison. Bluetooth was first created in 1994 as an alternative to data cables, for exchanging data through radio transmissions. Reaching consumer technology in 2000, Bluetooth has been one of the standards for music and audio streaming around the world.
Bluetooth is simply a wireless communication protocol for connecting devices and allow the wireless transfer of data. Slower than Wi-Fi, Bluetooth isn’t totally applicable for all use cases, but is generally very simple to setup and works across a wide range of devices such as cell phones, headphones, headsets, tablets, computers, remotes, and printers.
Going through many renditions, we’re finally up to Bluetooth 4.2 which has seen improvements in transfer speeds, security and reliability throughout the years. Some of the unique benefits of Bluetooth include the ability to connect up to 8 devices at once, and a user experience taken for granted – with one of the easiest ways to connect and pair devices, sometimes requiring only a 4 digit, or more, custom PIN.
Comparing The Two:
1.Effective Range
To compare the two, it makes sense to break down into a few specific categories that influence the use case of each standard. Since the purpose of adopting a wireless standard is to take advantage of freedom and distance, a logical place to start seems to be the effective range of both standards. In fact, the range capabilities of these two technologies is one of the largest differences between the two.
Bluetooth is interesting in that it uses three different classes, based on power sources available, and which class is utilized will of course change the range.
- Class 1, often used for desktop computers and laptops, will have a range of about 330 feet (or 100 meters)
- Class 2, often used by smartphones, has a range of about only 33 feet (or 10 meters)
- Class 3, most commonly used for other, smaller devices like mice and keyboards has an effective range of only 3 feet (or 1 meter)
Most Bluetooth devices will be Class 2, and will then have an intended range of about 10 meters, or 33 feet. This wouldn’t be much of an issue for those looking to stay in their office, or utilize a headset with their smart phone – if your phone is in your pocket, and headset on your head, you shouldn’t be wandering out of range. However, a limited range of only 33 feet can be far less than what some expect when they are considering a wireless phone for the office.
DECT, on the other hand, is the absolute king when it comes to overall, effective range. While each DECT phone will have their own specific range, the limitations will be on the phone itself, and the more common phones will generally hover around 300 feet. However, we have seen some more high end phones that will boast of a range of up to 500 feet. This will of course also differ based on climate, walls and physical objects block signals, as well as any interference. If too many base stations are placed too closely, or all channels of a base station are taken up by phones, some interference issues may arise.
2. Security Measures
Security is of a very high concern for the large business and enterprise market, and should be equally as important to the smaller businesses as well. Thankfully, when it comes to security, both Bluetooth and DECT have you covered. Each standard utilizes high levels of authentication and encryption to ensure that your data will be protected and secure throughout transmission.
- Bluetooth utilizes 128-bit encryption
- DECT utilizes a lesser 64-bit encryption
While DECT only utilizes a lesser 64-bit encryption, both levels of security are more than enough to ensure your data will stay jumbled, and an unreadable mess for anyone trying to poke their head in and eaves drop on your calls. Thankfully, encryption is not a simple matter of bigger is always better, and more behind the scenes information would be needed to understand the underlying encryption algorithm. However, safe to say, both Bluetooth and DECT will manage to keep all of your voice data safe when traveling through the airwaves.
3. Compatibility and Connectivity
Of course compatibility is a major point to consider as well, with Bluetooth one of the most popular standards its simple to find a Bluetooth enabled phone, headset, computer or even purchase a Bluetooth adapter. DECT, on the other hand, is a slightly less used standard for other devices besides a phone, headset or base station for these devices. However, that is not to say that DECT is foreign and under used.

Like I said before, Bluetooth can actually connect up to 8 devices at the same time, so your headset could be connected to a computer, smart phone, and desk phone all at once. Meanwhile, a DECT device can only connect to the base station – which then provides a connection to the network. So if absolute flexibility is key, Bluetooth has a bit of an edge there.
When it comes to connections, however, it is noteworthy that Bluetooth was previously developed as a means to transfer data specifically, and not so much voice. While the process will turn your voice and conversation into data to be transferred, as anyone familiar with VoIP knows, if this data transfer is slow or interrupted, it will lead to jittery, garbled phone call with stutters and awkward jumbled sentences.

DECT was developed specifically for telecommunications, and was even redeveloped for the US as DECT 6.0 to ensure the least amount of interference and interruption to your phone calls as possible. Bluetooth was designed as a means to transfer data, and not just specifically voice.
So, Bluetooth or DECT?
The DECT vs Bluetooth debate has been a long one, and the decision to adopt either Bluetooth or DECT as the wireless standard for your office will mostly come down to you and your office’s needs. Each has its strengths, and slight weaknesses, but this isn’t truly a case of one absolutely defeating the other.
DECT:
- Designed with a focus on telecommunications and stronger use case for voice
- Can only connect to a base station and one other device
- Still secure-enough 64-bit encryption
- Range specific to each device, but capable of 300 to 500 feet in most cases
If users only need to have their headset to work with a desk phone or computer based softphones, chances are DECT is the way to go. DECT would also make sense for open offices, or those particular to wandering around to take full advantage of the massive range DECT provides. DECT makes a lot of sense for call or contact center agents.
Bluetooth:
- Can have a total of Eight devices connected at once
- A more secure 124-bit encryption connection
- Has a wider use with a greater choice of compatible devices
- Class two range is limited to about 33 feet
Bluetooth makes total sense when headsets will be used with desk and mobile phones, or any other devices. Because of a wider range of capability, Bluetooth makes sense if your workforce is more mobile and works remotely. For these teams, the ability to take their headset with them will be key. Range can also be mitigated when using a headset with a mobile phone, because we all keep our cell phones in our pockets anyway.