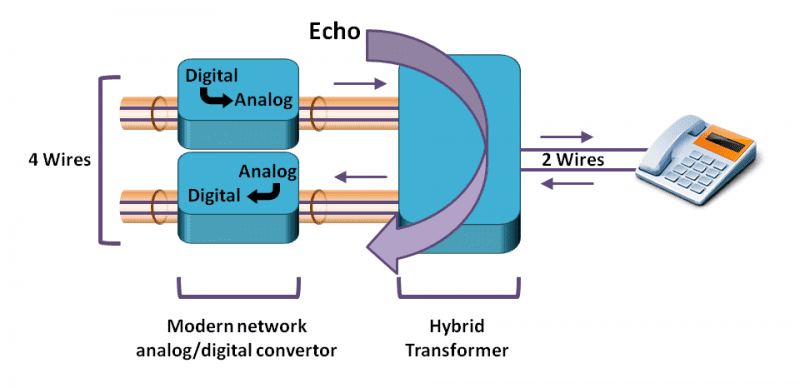
Echo during a phone call can be extremely irritating. Though this problem occurs on traditional phone lines as well, it can become very noticeable when using VoIP services. An echo effect is typically due to a blockage or mismatch, which results in the signals bouncing back from where they came. Additionally, the presence of echo effect in VoIP can be traced back to the functionality of the line. Where standard lines function with a delay of 10 milliseconds, VoIP can have up to 400 milliseconds of delay. As a result, the echo effect is that much more noticeable.
While most echoes in VoIP come from the far-end point, there are many other factors that can cause this to occur. In trying to prevent this undesired effect, we have put together a list of some of the biggest causes behind echo in VoIP.
Hardware – Hardware can especially be a contributing factor in creating echo. Faulty hardware can typically be found at the far end of the talk. Interference can be due to a number of reasons such as poor quality splitters, poor or damaged wiring, long runs of mangled telephone cabling, or even shoddy analog headphones. When each and/or any of these hardware problems exist, they can create a blockage or mismatch causing the signal to bounce, resulting in an echo.
Feedback – Feedback typically occurs from the far end telephone, and usually results in the voice traveling back to the mouthpiece from the earpiece through the receiver itself. This can occur when the caller is not holding the handset correctly (against his or her head) or if the handset is poorly designed. When either occurs, it’s possible for the microphone to pick up sounds from the earpiece and send them back down the line. Though this could be pegged as a hardware issue, as this occurs as a result of cheap or poorly designed hand/headsets, feedback is a separate concern in and of itself.
Intensity and Volume – Though echo can be detected when the delay from the original source is around 10 ms, the intensity of the echo wave determines how noticeable the echo will be. The return wave is almost always less powerful than the original, and therefore it should not be more than 65 ms, or over 30dB of attenuation. In addition to the intensity of the wave volume can contribute to corruption of the signal. Adjusting the volume of the phone itself can sometimes have an impact on echo.
Electromagnetic Interference – This type of interference can occur when one positions their systems too close to other electronic devices. Devices such as computers, power strips, and monitors have large electrical fields which can cause interference. Furthermore, other devices can create electromagnetic fields, so it is best to position your systems with this in mind.
Though there are other contributing factors, like design for instance, the above are the most common causes of echo in VoIP systems. While many VoIP providers offer echo suppression or cancellation features, there are also ways to avoid the problem all together. Many of the above causes can serve as ways to troubleshoot one’s system if they are experiencing this problem.
Related Articles:
– What Is Echo Cancellation?
– What is the Minimum Required Speed for VoIP?



![What is Omnichannel Customer Service? [Benefits & Tips] What is Omnichannel Customer Service? [Benefits & Tips]](images/omni-channel-explained-350x203.png)